How the game was administered. Continue reading
The governing body for competitive bridge in North America (and a few islands like Bermuda and Hawaii) was the American Contract Bridge Association (ACBL). Its headquarters was in Horn Lake, MS, a suburb of Memphis. The ACBL sponsored three national (actually continental) tournaments in different locations every year in March, July, and November-December. These were the spring, summer, and fall North American Bridge
One of the primary purposes of the ACBL was to provide the rules for distribution of masterpoints, which, depending on the event could be black, silver, red, gold, or platinum. Nearly every player aspired to attain the rank of Life Master, which, when I started playing required an assortment of masterpoints totaling 300. In 2011 the needed total was changed to 500, and the number of silver and gold points was increased.
When I began playing in 2004 there were eleven ranks:Rookie, Club Master, Sectional Master, Regional Master, NABC Master, Life Master, Bronze Life Master, Silver Life Master, Gold Life Master, Diamond Life Master, Platinum Life Master, and Grand Life Master. In 2011 the rank of Advanced NABC Master was created for players who had achieved 500 masterpoints but did not meet the other qualifications for Life Master status. Later the rank of Ruby Life Master was inserted between Silver and Gold, Sapphire between Gold and Diamond, and Emerald between Diamond and Platinum. That increased the number of ranks to fifteen.
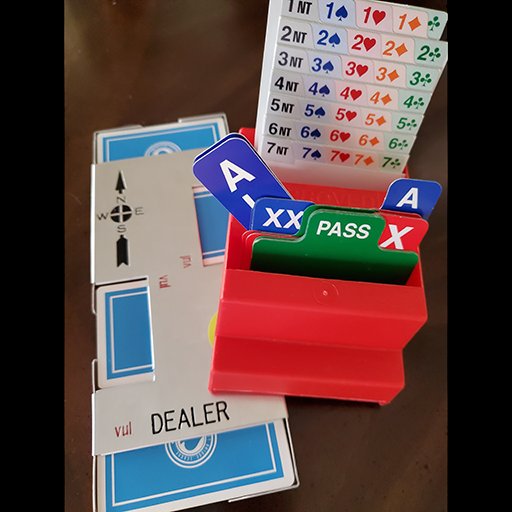
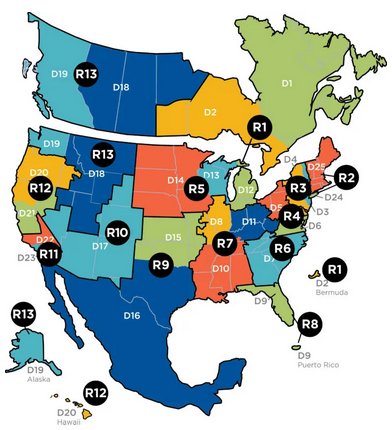
Geographic organization: The ACBL was organized geographically into twenty-five districts. The six New England states comprised District 25. The governing body for District 25 (D25) was the New England Bridge Conference (NEBC). Prior to 2020 each district elected one person, the District Director, who served on the ACBL’s Board of Directors.
Each district was divided into units. D25 had eight units—one for each of the less populous states and one each for western, central, and eastern Massachusetts. The unit for Connecticut was identified by the number 126. Its governing body was the Connecticut Bridge Association (CBA). The other units had similar appellations and three-digit numbers. The most populous by far was EMBA.
The lowest level sanctioned by the ACBL was the club. Most clubs were owned by one or two people. The Hartford Bridge Club (HBC), which was the oldest continuously operating bridge club in North America, was one of the few that was owned and operated by its members.
In 2020 a new geographic entity, the region, was created for the purpose of reducing the size of the Board of Directors for twenty-five to thirteen. D25, 24 (NYC and Long Island), and D3 (northern NJ and eastern NY) were combined into Region 2. The Regional Director (RD) was elected by the units within the region, but the person so elected was not supposed to represent his/her constituents. Instead the RD was charged with promoting the interests of all members.
Masterpoints: Winners and high finishers in club games ordinarily received black points. The units could sponsor sectional tournaments that awarded silver points in larger quantities than club games did. The districts could run regional tournaments that awarded red and gold points in still greater quantities. The most valuable points for achieving Life Master status were gold and silver.
The primary way to receive silver points was to attend a sectional tournament sponsored by a unit. Most units in D25 ran several sectionals per year. Three or four weeks a year Sectional Tournaments at Clubs (STaCs) could be run at clubs within the participating unit. These events also paid silver points. At some point in the teens the ACBL began to sanction sectional tournaments on cruise ships as well.
The primary way to receive gold (and much less important red) points was to attend a regional tournament sponsored by a district. Through 2019 D25 ran five regionals per year. The NABCs also included regional events that paid gold and red points. At some point in the teens the ACBL began to sanction regional tournaments on cruise ships as well. My wife Sue and I went on one in 2012 (described here). We signed up for a second one in 2020 (described here).
Administration: The ACBL and each of its units and districts were not-for-profit organizations. The ACBL itself was, in theory at least, run by the Board of Directors, who were bridge players. The day-to-day operations of the organization were run by salaried employees, most of whom knew little about bridge. Aside from running the three NABCs, the ACBL also hired and trained the Tournament Directors who administered each event at tournaments. It also tested and certified directors for club games.
The governing body of the New England Bridge Conference was its Board of Delegates. Its members were chosen by the units. It only met twice a year. Its main responsibility was to elect the four officers: president, vice-president, secretary, and treasurer. Most policy-level decisions were made by the Executive Committee, a group that met several times a year. It consisted of the four officers and representatives of each unit (two from the CBA and EMBA). The president appointed the tournament manager, the webmaster, the tournament coordinator, and committee chairmen and members. The most important committee was the Tournament Scheduling Committee. The district also had a director-in-charge and and Intermediate/Novice chair. Those roles were held by Peter Marcus and Sue Miguel for all the years that I was involved.
The governing body of the CBA was its Board of Directors. This group was elected by attendees at a designated tournament. It consisted of the same four officers as the distric, the past president, and twelve representatives, eight of whom were from specific regions. The president appointed the tournament coordinator, the list manager, the webmaster, the unit coordinator, and STaC chairman.
Bridge clubs had a manager and at least one director. The former administered the club, and the latter ran the individual games. At many clubs the director and the manager were the same person. The Hartford Bridge Club was administered by a Board of Trustees, all of whom were elected at an annual meeting. It had the same four officers and a set of six trustees. The Board met once a month. The manager of the club had been Donna Feir for as long as anyone could remember.
The games: All competitive bridge games are “duplicate”, which means that each pair’s results are compared against other pairs playing the same cards. The most common form was pairs, in which each pair of players competes against other pairs. The scoring was rather simple. Each pair gets one point for each pair that it outscored on the hand and a fraction of a point for each pair that it tied (one-half if two pairs tied, one-third if three pairs tied, etc.). Adjustments were made if the same number of pairs did not play all the hands. Almost all club games were pairs games.
It was also possible for four people1 to compete as a team in various formats. They were explained in detail here. A few large clubs—such as the HBC—scheduled and ran Swiss teams events. They were usually quite popular.
A third form of the game, in which persons competed as individuals, became an endangered species in this period, but I had several interesting experiences with it.
Tournaments: Sectional tournaments ordinarily lasted last two or three days. They were ordinarily held at a hall owned by a church or ethnic organization, a senior center, or some other similarly large room. Usually the last day features one or more Swiss teams event. The other days are pairs. In general they must be run by a tournament director approved by the ACBL.
Regional tournaments ordinarily ran from four to seven days. They were generally held at a hotel with a ballroom or two and featured a mix of events. In most cases both pairs and teams events were offered at the same time. Traditionally the last day was devoted to a teams event of some kind.
Each NABC lasted for eleven days and featured a large assortment of events every day. Some were held at hotels; some were at convention centers. Traditionally the last day featured a very large teams event of some kind.
People sometimes attended tournaments without a partner. The administrators of tournaments tried very hard to find a suitable match for each such person.
Equipment: Bridge was, of course played with a deck of fifty-two cards. Four people sat around a card table. Competitive bridge required a little more equipment. In a social game the cards were shuffled after each hand. In duplicate bridge the cards were kept in carriers (usually called boards) made of plastic or metal to keep the cards used by each player (North, South, East, or West) separate so that they can be played by others siting in the same direction.
At tournaments and large clubs the boards were created by dealing machines, and scores were entered on hand-held devices called BridgeMates.
In duplicate bridge the bids were made by selecting card from a bidding box. Players were also required to make available an official convention card that explains the meanings of their bids.
High-level events at NABCs sometimes positioned the players behind screens. In that case players did not talk among themselves at all. The purpose was to minimize the opportunity for cheating. Nevertheless, some players were caught doing it.
Online: At some point during the teens the ACBL recognized a game with rules and behaviors similar to those of bridge that was played on the Internet. A website called BridgeBase Online (BBO) signed an agreement that even allowed its users to win masterpoints on their website. I hated this game and refused to call it bridge.
1. In events that last two or more days teams could have five or six members.

 2008-2020 The Organization of Competitive Bridge
2008-2020 The Organization of Competitive Bridge






Pingback: 2022 Bridge: Sectional Tournaments | Wavablog