A complicated system. Continue reading
People who have not worked in retail advertising will probably have trouble understanding this entry. Nevertheless, because the AdDept system was the focus of my life for so many years, I feel obliged to document as much of its structure as I can remember. It did not occur to me that I might want to undertake such a task until very recently. Consequently, when I closed down TSI in 2014 I discarded almost all of the system’s documentation. The few computer files that I have subsequently found are mostly PageMaker documents. I don’t have that software on my computer, and the files are too large for the services that will convert them to pdf files online. So, I must rely on my memory, which is not as reliable as it once was.
AdDept was designed for and implemented in OS/400, the operating system of the AS/400 and its follow-on hardware. Some of the important and unique features of this operating system are described here. Every line of code that we wrote in 1988 still worked in 2014, and I have no reason to expect the code to stop working any time soon.
All programs were originally written in BASIC. Around the turn of the century IBM stopped supporting BASIC, but TSI was authorized to install the product (a compiler, and interpreters of both BASIC commands and BASIC procedures) on any system that use our software. This only caused one major problem, which is documented here. However, Denise Bessette did not like this arrangement and undertook to convert the programs to ILE RPG. I never appreciated the value of that idea, and I never took the time to learn that language, which is supported on no other system.
All data tables and the major programs in AdDept began with the letter D, which stood for department. This was for TSI’s benefit. The ad agency system used a similar structure, but no files or programs began with D. The second letter in AdDept tables was usually A, I, M, or P, which stood for accounting, (loan room) inventory, media, and production. Programs that were used for cleanup, copying, and other miscellaneous tasks began with DX.
All AdDept programs were stored in the same library1. It was usually named TSIPROG. The data was in a library named TSIDATA. A few clients had additional data libraries for additional companies. At these installations we created a separate library called COMMON or TSIDATACOM to hold the tables that were used for both companies. For example, both companies probably used the same ad types and expense classes (major media). The tables used by both were moved from TSIDATA to the common library. A new data library was created for the data files for the second company. In the beginning it contained empty copies of all of the remaining files in TSIDATA.
No two instances of AdDept were the same, but each had the same TSIPROG library. The settings for each installation were designated in two ways: 1) A set of empty one-byte files, the existence of which activated certain features; 2) a file called DASPECS that contained a very large number of switches, descriptions, and system values. The program to maintain the system values was not on a menu, and users were not allowed to run it.
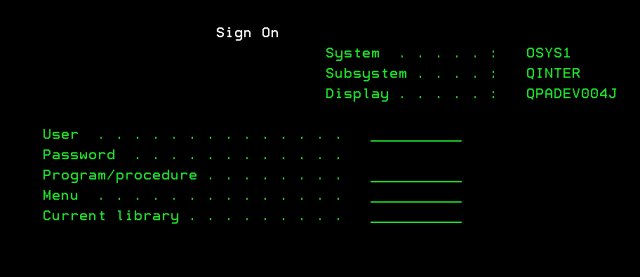
Everyone needed a user ID to sign on to the system. Those connecting through a network could have any number of simultaneous sessions open.
AdDept’s user table, which was also on no menu and could be run only by the AdDept liaison, limited the programs to which the user had access. If the same employee worked with two different data libraries, a second user ID was required. The two user ID’s would have different library lists.This arrangement may sound cumbersome to people who are used to managing hundreds or even thousands of nested folders, but it did not seem strange to the users of a multi-user system. Furthermore, it was absolutely critical that changes not be made on files in the wrong library. All TSI menus displayed the name of the data library to help eliminate confusion.
The retail calendar was accommodated by the season table. The key was a three-digit number. The first two digits were the fiscal year. The third digit was 0, 1, or 2. 0 meant that a standard twelve-month calendar was used. 1 and 2 were used for 4-5-4 retail calendars, which are described here. This table contained the name of the season, the starting date, and the number of weeks in the season.
Ads were classified by three separate codes:
- The one-digit insertion code determined which set of screens was used for data entry. This was a fixed set, but more codes could be added for additional media.
- The one-digit expense class identified how the ads were categorized for accounting purposes. Later a sub-class code (blank default) was added for one client.
- The two-digit ad type was specified when an ad was created. This table held the insertion code and expense class. It also had a binary field to identify whether color charges were applicable.
Media vehicles, such as newspapers, magazines, and broadcast stations and networks (called pubs in AdDept), were identified by a five character codes combined with a two-digit number (usually 0). For newspapers at least one number was reserved for inserts (usually 10). The users specified the days on which the paper published, whether it was AM, PM, or a combo2 and the paper’s depth (maximum number of inches vertically on a page). For direct mail the pubs were usually geographic markets.
Stores could be identified by a five-digit number.
Every pub had a list of stores that were associated with it. There was also a date-sensitive pub-store allocation table that contained the percentages allocated to each store associated with the pub. The key to this table included an effective date. Less than half the AdDept retailers allocated costs to stores, but the ability to do so was very important to those that did.
Rates for ROP and inserts were date-sensitive. For ROP separate rates could be entered for black-and-white and several different color choices. There were also tables for linage-based discounts and premiums for things like special positioning such as “back of main”—the last page on the first section of a paper. For inserts a table of usual quantities (thousands of copies) could be created, with rates for each.
The system needed to be able to find the right rate to apply whenever an ad was changed or moved. Costs could also be recalculated en masse when a new contract had been negotiated. These were attractive features.
Probably the best idea that I had when designing the system was to allow the definition of pub groups (identified by five-character codes) to specify sets of pubs in which the same ads often ran. Clients could have hundreds of these or none. When a new ad was created, one pub group could be specified. A schedule could automatically be created with all the pubs in the group.
The hierarchy of participating merchants had five levels in AdDept. The lowest (most detailed) was the department. The system called the other four ADMGP, GRPVP, SENVP, and GRSEN to match Macy’s East’s designations. Most retailers had only two: DMM’s and GMM’s. The May company used “CCN numbers” to group related departments. For each level each client determined the descriptions used on screens and reports.
Employees were identified by three-character codes. Employees could be assigned to production jobs. So, an employee could see a list of all of his open assignments.
The traffic system allowed specification of a code for each production job that determined the job’s production schedule. So, black-and-white ROP ads might have a three-week production schedule with eight steps. The number of days for each step could be specified. Then the system would count backwards from the release date to build a schedule of due dates that accounted for weekends and holidays. The completion dates of each could also be entered (an X meant “today”).
This seemed important to several clients, and we built it precisely the way it was described to us. However, the production employees did not like it. For one thing, most of them used Macs for working on the ads, and they found a text-based system clumsy. I don’t honestly think that they would have liked it much better with a GUI (graphical user interface) as the front end.
The accounting tables were similar to those in the GrandAd System (described here) or any other system. They were designed to be consistent with whatever system was used by the accounting department, but AdDept users did not need to memorize the very long codes that were common in those systems. In AdDept the main entity was the sub-account, which was identified by a five-character code. One corporate G/L account was specified for each sub-account.
The vendor table also had a five-character key. The corporate vendor number was specified there. This table was used for merchandise, media, production, and other vendors.
Categories of production costs were identified by three-digit codes, just as in the GrandAd system.
The Ad Files
The system had one major header file for ads of all types and a number of lists that were associated with it. The ads file3 was identified by the season, a five-digit ad number (usually generated by the system using client-specific rules), and a one character version code (usually blank). The ad number could either be entered or generated by the system. Data entry began with the specification of the run date and ad type. A large amount of information was deduced from those two values. The headline and size4 of the ad were then entered on the header screen, which also contained many other fields.
The second step for ads of all types was the media schedule. If the pub group was accurate, nothing had to be entered here for ROP and inserts. For direct mail the quantities by market were entered.
The third step was the list of participants with percentages and co-op commitments.
Expected production costs could either be entered as one lump sum or detailed by category.
Audit Trails
History records were created for any activity that affected planned, committed, or actual costs or income. Reports and screens were written for viewing them. A few custom reports were also written for clients.
Planning
New ads were ordinarily assigned a status of P, which stood for “planned”. When the plan was completely approved, a program could be run to change the status of all status P ads to A (active). At the same time records of the detail of the costs of those ads at that time were recorded in separate files named DAPLAN (by department or group) and DAPLANST (by store).
Changes could still be made to any aspect of any ad, of course. Those values were considered “committed”. The actual costs were based on the measurements and the invoices from the media and production vendors. Actual co-op was based on the “claims” that had been processed.
In subsequent years several AdDept users let the system build the entire schedule based on the previous year. Thus season 951 could be built based on the ads run in 941. This process was called “anniversarying”.
Cost Accounting
Most advertising departments were keenly interested in comparing planned, committed, and actual costs by merchant or by store. AdDept had programs that would create detailed records every night by store and/or merchant for all ads in the current season. The merchant records were stored in DACOMMD (committed) and DAPANDL (actual). The records by store were in DACMDST and DAACTST.
Numerous reports were written to allow comparison of planned, committed, and actual costs and income (from co-op). Some users also queried these files on a regular basis using IBM’s Query/400 product.
Interfaces
Broadcast ads could be fed into the system from Doner, the May Company’s ad agency, and from Media Management + files created either internally or by an agency. There may have been one or two others of these.
A couple of clients used ad agencies for their newspaper ads. TSI constructed interfaces to receive the ad schedules from the papers.
Several interfaces were created to send files to feed corporate Accounts Payable and General Ledger systems.
Sales at the department level could be downloaded from the mainframe. Customized reports helped gauge the effectiveness of ads in comparison with the costs.
Backup
It was easy to schedule a backup nightly and to schedule the cost accounting programs to start when the backup was done. The backup would not save files that had record locks. Any time that a record was read from a program that could update that file (as often occurred), the record was locked to prevent one user from accidentally overwriting the work of another. It was sometimes difficult to persuade users either to make sure that everyone had signed off every night or to shut down the interactive subsystem before backing up and restarting it later.
TSI recognized this problem and warned the users about the possibility of lost data if files were not backed up routinely and correctly. We even offered (for a modest fee) to check their backups every day and notify them by telephone if the backup for the previous nights did not complete correctly. Only one client took advantage of this service.
The failure to check backups resulted in one ugly mess that was described here.
Cleanup
By the standards of the day the cost accounting and history files often became extremely large. A menu of programs that permanently deleted records from old seasons was provided.
Other Modules
The Loan Room inventory system was successfully used by Macy’s East for approximately twenty years.
A Photo Shoots system was also designed for Macy’s East, but it was never implemented. I don’t remember why they lost interest in managing the activities of their studio. The location of the studio in Newark may have been a factor.
Many modules were developed for Belk. One that I remember calculated the store’s use tax liability for direct mail pieces for each jurisdiction.
Saks Inc. in 1999 wanted TSI to design a very complicated system for collecting data from the systems of each of its divisions and, eventually, to produce reports that compared divisions. I was very happy that nothing came of this idea.
A special module was created for Radio Shack to manage its advertisements in magazines.
I suspect that there must have been a dozen more of these modules that I cannot recall. We delivered hundreds of custom programs over the years and quoted a similar number that were never approved.
AdDept was a fabulous system. Because it contained so many features, it was somewhat difficult to demo. The screens and most of the reports were ugly. Nevertheless, as soon as prospective clients understood its potential, it was easy to sell to anyone with a budget.
Unfortunately by the time of the Bush-era Great Recession in 2008, Tarot card readings for most major retailers—especially the ones that did a lot of advertising—began with the thirteenth trump card: Death.
1. “Libraries” were a type of object on the AS/400. They were places to store other objects in the same way that folders or directories are used on PC’s. However, it was not possible to build a “tree” of libraries. All other libraries resided in the QUSR library.
2. Yes, a few papers still published two editions per day in the nineties.
3. As far as the OS/400 was concerned, DMADS, the ads file, and the files that contained all of the lists were equivalent to the tables. However, TSI’s organization and documentation drew a useful distinction between the relatively stable tables that were defined at the beginning of the installation and the much more volatile ad files and transaction files.
4. The size for ROP ads was entered in columns and inches. A full-page broadsheet ad was entered as 6×21. The program knew to adjust the inches to match the paper’s depth. The size for inserts was entered in terms of thousands of copies. The size for broadcast ads was the length of the spot in seconds, usually 15 or 30.






































 Needless to say we are concerned about what effect the realignment will have on TSI. We have spent the last 17 years developing AdDept, the software product which has become the standard of the industry for administration of retail advertising departments. The May Company was our largest client.
Needless to say we are concerned about what effect the realignment will have on TSI. We have spent the last 17 years developing AdDept, the software product which has become the standard of the industry for administration of retail advertising departments. The May Company was our largest client. Since that time, as I wrote you earlier, most of the rest of the department stores in the country—as well as several other large retailers like Dick’s Sporting Goods—have successfully implemented AdDept in their sales promotion departments. They were able to get affordable systems tailored to their requirements. AdDept is not a sexy system, but it gets the job done.
Since that time, as I wrote you earlier, most of the rest of the department stores in the country—as well as several other large retailers like Dick’s Sporting Goods—have successfully implemented AdDept in their sales promotion departments. They were able to get affordable systems tailored to their requirements. AdDept is not a sexy system, but it gets the job done.