The beloved Databurger. Continue reading
In July of 1981 IBM announced a new system for small businesses. It replaced the system that we were familiar with, the IBM 5110/5120. Outside of the people who programmed software for small businesses, the unveiling of the System/23 Datamaster was greeted with very little enthusiasm. For one thing the model that IBM was promoting looked very much like the 5120. The cost was half as much as the 5120, but it was still a lot more than what people were paying for “personal computers” that were marketed by competitors. Most people eagerly awaited IBM’s approach in that market.
That answer would come in a few months. To us at TSI the Datamaster was just what the doctor ordered. The information about this system on the Internet is shamefully incomplete and, in a few places, erroneous. Here are details of the original announcement.
- The processor was an eight-bit 8085 chip from Intel, which was a little bit surprising. IBM did not usually outsource processors, and the 5110/5120 used a sixteen-bit processor. The 256K of memory seemed more than adequate.
- The only programming language supported was BASIC. Nevertheless, IBM offered no method of converting programs from the 5110/5120. This did not bother us much, but software companies that had put a lot of effort into systems for those computers were not happy.
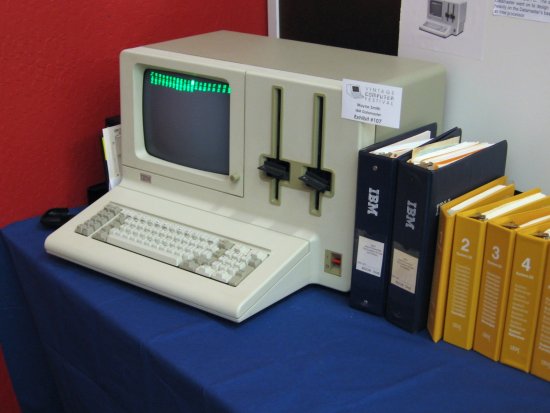
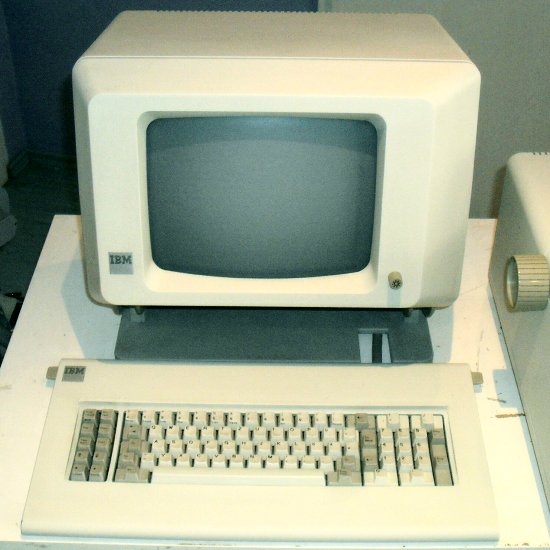
- There were two models. The 5322 looked a lot like a 5120. The 5324 came in three pieces. Its processor and diskette drives were housed in a standing steel box the height of a two-drawer file cabinet. The display and keyboard for the 5324 were separate.
- The displays for both models used green letters on a dark background. Research had shown that this was slightly easier on the eyes than other combinations. This was somewhat important.
- Two CPU’s could be connected to a box that held two additional diskette drives. We never saw anyone who purchased this box, which was benerally called a “toaster”.
- IBM supplied several business applications, including accounts payable, general ledger, and payroll. We worked with several customers that had bought these packages. In general they found them extremely cumbersome and painfully slow.
- A word processing program was also available from IBM. Unlike the business applications, the word processor was extremely good.
- At first only two printers1 were available. Both were dot matrix printers. One printed at 80 characters per inch, the other at 120 characters per inch. Only idiots bought the 80 cps one, but it allowed IBM to quote a lower base price.
- The most important change as far as TSI was concerned was that the BASIC interpreter allowed variable names of up to eight characters. This was a huge improvement over the 5110/5120, which only allowed one character and an optional digit.
- The BASIC interpreter was also changed to allow up to five digit line numbers. There were a few other improvements as well. I don’t remember all of them, but I remember being very impressed with what we would now be able to do.
- The system came with a set of templates that fit at the top of the keyboard. Each template displayed what it meant to use the key labeled “Cmd” and one of the keys. Every system command, every BASIC command, and every operation of the word processing program could be accessed by pressing two keys. This feature made it possible even for people who were not good typists to key in long BASIC programs very rapidly.
- The components of the system were of very high quality. Many of our customers used the systems for years without ever encountering problems with hardware or the system software.

I don’t know the date of the additional features, but they came within a year or so
- A letter-quality printer that used a daisy-wheel. In my opinion, the addition of this printer made the Datamaster the best stand-alone word processor available. It was certainly superior to the Displaywriter that IBM sold for that purpose. When we got one, we used it for all of our word processing (and everything else) for many years.
- A hard drive unit that could hold up to 30 megabytes. Up to four Datamasters could be attached to it. The software for record-locking had already been delivered in order to make the toaster usable by two Datamasters. So, the delivery of the hard drive made the Datamaster a true multi-user system. Also, access to the hard drive was much faster than to diskettes. Reliable PC networks were still years in the future, and the PC’s themselves were notoriously subject to the dreaded “blue screen of death” and other catastrophic failures.
There were, of course, some severe limitations. Most of them were similar to limitations that the users of the 5120 also faced.
- All of the hardware interfaces were unique and strange. This made it difficult, if not impossible, for third-party hardware vendors to develop printers or anything else that could attach to the computer. IBM had done this for years, but Datamaster prospects were not accustomed to this approach.
- There was still no way to communicate with the system remotely. This meant that it was very difficult to market a software system to customers outside of driving distance.
- There were no subprograms that could be called repeatedly as routines. Programs could be linked together, but all the needed data also had to be passed. The first program was erased from memory when the second was called. So, commonly used routines—such as date functions—needed to be built into every program that needed them.
- There was no text editor with a search function.
- The system had no graphical capability at all.
- Calculation-intensive applications were so slow that no one could possibly use them. One company developed and tried to market a spreadsheet program through other software vendors. The instructions for showing the software to a potential client highlighted the places in which the person doing the demo should have some patter ready to distract the prospect from watching the screen. I would not have been able to keep a straight face.
- The only backup medium was diskettes. We dreaded when users backed up because they sometimes designated the wrong drive as the target.

From TSI’s perspective one of the best things about the Datamaster was that the IBM sales reps were suddenly eager to work with software companies. They could sell Datamasters to many diverse businesses, and the starting price had been cut in half. They brought us in to meet with prospects, but only when the IBM software packages were not applicable. Therefore, we ended up creating systems with little chance of being appropriate for more than one customer. It was enjoyable and satisfying work, but not very profitable.
Eventually IBM started a Value-Added Remarketer (VAR) program that allowed software companies with qualifying products to sell Datamasters. When that happened, the IBM reps treated us as competitors even though they got some credit for our sales.
1.There was really only one printer. The slow one could be “field upgraded” by an IBM customer engineer who made a slight adjustment to speed the printing.