People and events at SRI/Stage Stores. Continue reading
Everyone with whom I dealt—and there were a great many people over the course of seventeen years—-called the large retailer based on the south side of Houston “Stage Stores”. Even their LinkedIn pages refer to Stage Stores. However, our contracts1 were definitely with a company named Specialty Retailers, Inc. (SRI). The checks that we received were from SRI. This always seemed strange to me, but I managed to piece together from various sites on the Internet something of an explanation.

SRI was incorporated in 1988. I was unable to discover who the original stockholders were or who ran the corporation. I also have no idea what, if anything, SRI did in its first four years of existence.
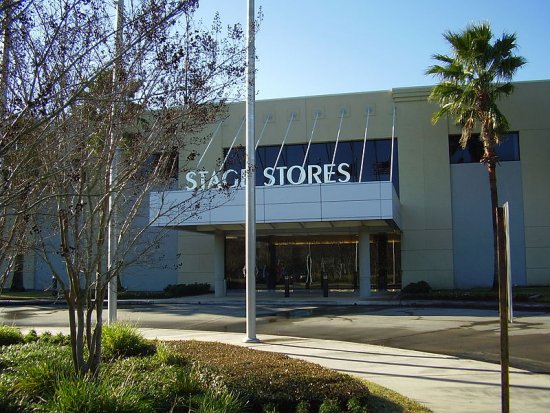
In 1992 the company purchased a Colorado-based retail company named Fashion Bar, Inc., which had seventy-one stores. The larger ones were branded as Palais Royal or Bealls2. The rest were known as Stage Stores. In the nineties SRI purchased a large number of other stores. Most of them bore the Stage logo. SRI’s headquarters at 10201 South Main3 in Houston was known locally as Stage Stores, and that name, as you can see in the photo, was displayed prominently over the entrance. The only stores that were actually located in Houston were branded as Palais Royal. I recall actually purchasing a leather belt in one of them. Many people in Houston knew about Palais Royal, but Stage Stores and SRI were probably not on their radar.
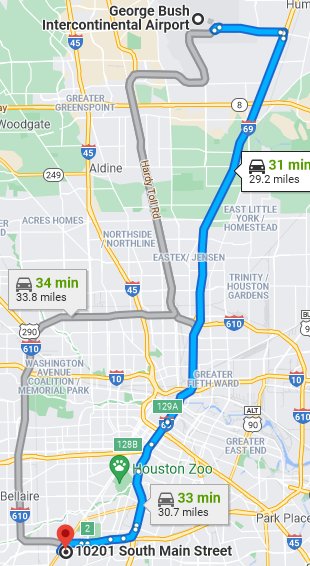
In late 1996 or early 1997 Doug Pease, TSI’s Director of Marketing, received a call from Brenda Suire4, the Director of Finance for Stage’s Marketing Department. Doug and I flew on Continental Airlines to Intercontinental Airport in Houston to meet with Brenda and some other employees. We were somewhat surprised by the length of the drive from the airport to Stage’s headquarters.
The blue route on the map at left suggests driving through downtown Houston. That route would only be considered if the trip was in the middle of the night. We always took the western loop on I-610.
On the second day in Houston I demonstrated the functionality and design of the AdDept system at the local IBM office. It went over very well.
I recently found in my notes from January of 2001 some of the items that were included in the contract that resulted from that presentation and subsequent negotiations.
I was surprised to discover that in 1997 Stage paid us over $8,000 for the expense payables, sales, MM Plus, and AdSEND (!) interfaces. No wonder we made so much money in those days. We have no choice but to give them the assistance they need to get the first three working. They don’t use AdSEND any more, thank goodness, and I am pretty certain that no one remembers that they paid for this. I don’t remember coding an expense interface for Stage, but we clearly did it in 1998.
As part of that initial contract the programmers at TSI wrote a great deal of new code. Stage Stores had more stores and fewer merchandise departments than the first few AdDept customers. In most of their markets they operated only one store. They were therefore much more interested in the ratios of media dollars spent on each store to the amount of sales that the store generated than in sales and expenses by department. To provide this information we wrote code to accept sales by store from the corporate systems. We also wrote a set of reports that showed the ratio of advertising expenses to sales for each store.
No one at Stage Stores had previously examined the broadcast (i.e., radio and television) advertising too carefully. The buys and audits were done by a lady (I don’t recall her name) from Reynolds Communications. She used SmartPlus5 software to make the schedule and audit the spots that each station ran. Stage soon discovered that she had been spending much too much money on television buys, especially in one-store markets in Louisiana. She knew that the company had a store in those markets, but she had no access to sales data.
As often seemed to happen in AdDept installations, this unexpected revelation allowed Stage Stores to save enough money on an inefficient use of funds to justify most of the cost of the entire system.
Training and installation: In 1997 Stage sent three employees to TSI’s office in Enfield for several days of intensive training: Brenda, Floyd Smith6, and Hugo DuBois7. The emphasis of the training was on how to get the most out of the AdDept software in their environment.
Floyd was Brenda’s right-hand man in the business office. For the first few years—which (for reasons unrelated to the system) were rather chaotic—Floyd was the liaison between TSI and Stage. Hugo, a native of Belgium, managed the department’s local area network. He mainly worked with the production and creative people. I am not sure why he came to Enfield. Hugo’s only role in the project was to connect the network to the AS/400 and to install and configure the software on individual PC’s and Macs so that the department’s employees could access the AdDept system.
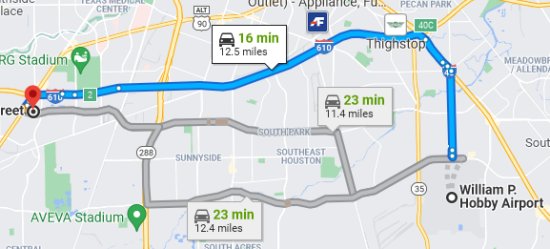
After the AS/400 had been delivered, and the network was connected to it, I flew to Houston to install the AdDept software and configure the database. Over the next few months I returned to help them deal with problems, to show them how to use new features, and to gather ideas about further development. I soon discovered that there was a better way to get from Connecticut to Stage. On most trips I flew on Delta or American and landed at Houston’s smaller airport, Hobby. Not only was it much closer to Stage, but there was usually a better choice of flight times.
Within a year or so the system was running fairly smoothly. Then in 1998 Brenda left Stage Stores, and for a while Floyd ran the advertising business office. His primary assistant was Toni Young8. One of the primary AdDept users was Renee Mottu9, who managed the expense invoices.
Fortunately for TSI, for the next year our involvement with Stage was reduced to answering phone calls and resolving mundane issues. I say “fortunately” because even though Stage Stores declared Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 1999, the effect on TSI’s bottom line was minimal. The effect on daily life in Stage’s advertising department was for a considerable period much more severe. My notes after a visit to their headquarters in January of 2000 stressed that “Those poor people spend half of their time trying to persuade newspapers to run their ads.”
Brenda was replaced by Karen Peltz, who had held a similar position at Foley’s10, the chain of department stores owned by the May Company that was also based in Houston. At the time Foley’s had been using AdDept to solve various problems in its advertising department for five years. I had worked with Karen at Foley’s, but only a little. Eventually Floyd moved to another position at Stage Stores, and Toni Young managed the day-to-day operations of the marketing business office thereafter.
I had only a few interactions with Joanne Swartz11, the Senior VP of Marketing, and the guy who was Advertising Director. I do not remember his name. I think that Karen reported directly to Joanne.
I dealt with two people in the media area. The woman’s name was Deidre Prince11. I do not remember the guy’s name, and it is not in the notes. I also remember Sandra Green, who used AdDept for buying newspaper space. She seemed to have a lot more difficulty using the system than anyone else did.
My notes: I discovered quite a few email messages that I sent back to TSI’s office from Stage. They are dated between October 1999 and January 2001. I’ll start withe the earliest one
Not a great start today. I woke up at 6 AM. I got up and stumbled around the hotel room for a few minutes. I ironed some shirts and pants. At 6:55 I shaved. I looked in the mirror and saw Dracula. The blood was pouring from my lip. It took over 40 minutes for it to stop bleeding. I painted the New Skin on it. I got dressed and went to Stage. The New Skin held until almost 5 PM. Then I bled all over my shirt and pants, but this time I got it to stop in only about five minutes. Life on the road is so glamorous.
Renee Mottu is looking for suggestions as to how to remove two possums that have taken up residence beneath her mobile home. She rejected my idea of sending in a dachshund. She said that the possums would eat a dog.
I didn’t get to run tonight. Toni Young told me about a good trail. I put on my running duds, followed her directions, and drove around for about 25 minutes looking for the place. I never found it. I drove back to the hotel, got some food, and settled into my room to watch “Norm” and “The Drew Carey” show.

The first paragraph refers to a blue-black circle that appeared on my left lower lip in the nineties. It has never caused any pain, and it has not bled in the last decade or so. The story of Renee and her possum continued for a few visits. Before reading the above I had totally forgotten that for a while Norm McDonald had a network television show.
The following are from the subsequent two days on the same trip.
It was in the 80’s here yesterday, but it felt cooler. There was almost no humidity, which is rare for Houston. Floyd’s office was freezing. He has an electric heater in his office. We had it running most of the day even though we had six people crowded around his PC all day long. I brought sweaters, and I will wear one today.
Stage has network printers. We sent a 40-page report to Floyd’s printer about noon. It was still in SND status when I left at 6 PM. Floyd said it will sometimes not print until the next morning. Have they ever complained about this? I think the culprit may be the faxing. They were faxing all day yesterday.
I noticed at Stage that their floors must not be very level. The pieces of their desk units come together at angles. I also noticed that some units were raised off the floor as much as an inch on one side.
I don’t think that I could possibly in good conscience approve more than five months for the palm tree research project at this time.
How much do you think is the monthly fee that Reynolds Communications charges Stage to handle (including auditing and approving invoices from stations) their broadcast advertising?
I don’t remember the precise answer to the last question, but I am pretty sure that there were two digits to the left of the comma. The next set of emails came from the trip that began on January 11, 2000.
I was dreading the flight to Atlanta. I envisioned myself standing in line with the common people now that my silver medallion card has expired. I was delighted to discover that my ticket still says “Silver Medallion.” Half of the flight got on with the medallion status group.
The phone on my seat on the flight from Hartford to Atlanta has a little LCD display. It discloses the NASDAQ closing price every few minutes along with advertisements for various ways to spend your money on the phone.
A lady on the Atlanta flight has striped hair. Not streaks, stripes. She has brown hair intermixed with ½” blonde stripes. I guess it is a look.
The flight from Atlanta to Houston sat in the gate for about 20 minutes. Then we got in the usual long line to take off. It must have been over 100 degrees in the cabin by the time we hit the skies. The guy in the seat in front of me pushed his seat all the way back. I have therefore had to turn 45 degrees and put my laptop on my lap. Even so it is uncomfortable to type. Thankfully there is no one next to me.
Listening to Kiri Te Kanawa sure beats listening to salesmen. On my last few flights the planes were full of families and college students. The passengers on both of Tuesday night’s flights have been mostly middle-aged men.
I still have a 45 minute drive ahead of me after this flight, which won’t get in until about 11:00 central time. I need some caffeine.
I used the air conditioner in the car all the way from the airport to the motel.
… Renee Mottu asked me to hire her. I told her that we needed experienced, or at least trained, programmers. She pressed me on this. She said that she was sure she could learn programming and that Floyd would give her a good reference. By the way, she said all of this in front of Floyd.
I remembered to ask Renee what happened to the possums living under her trailer. She said they were still there. I repeated my recommendation about the dog. She said she didn’t have one. I said she should borrow one. She asked me (!) if I knew anyone who had a dog she could use. Later I heard her walking around intoning “Does anyone have a dog I can borrow?”
I think that by 2001 Stage Stores must have been emerging from bankruptcy and resuming their strategy of expansion by purchasing other chains. The biggest of those was the acquisition of Peebles, a chain of 125 department stores based in South Hill, VA.
For some reason the management at Stage wanted to keep track of all expenses and co-op income of the Peebles stores separately. This was the first, but not the last, time that I installed a second AdDept database on the same AS/400. There was still only one set of programs, but each user had two AS/400 user ID’s. Their profiles determined which database would be used.
Here are some of my notes from January of 2001:
The meeting in the afternoon went well. Joanne, the advertising VP introduced me as “the resident genius.” The project has been scaled down. We need to be able to do accruals at the store level for media and production at the store level. We also need to be able to do prepaid to expense. One unusual wrinkle is that they do not want to allocate creative costs to stores. They want to be able to get ratios of advertising expense to sales from AdDept, but we must be able to reconcile this with what is in the G/L.
I was glad that I was an outsider at this meeting. The politics was just barely below the surface. Chuck, who I think is the CFO, put Joanne on the spot about something that was not even on the agenda. Their explanations were not at all impressive. The experience had the happy effect of reminding why I did not like working at a larger company.
Toni Young says that she thinks that Renee Mottu never got rid of her possums.
It turns out that what Stage really wants to do most is to start using what they have and what we have previously proposed—SmartPlus interface, sales interface, and expense payables interface. They spoke of the SmartPlus interface as if it were a done deal. I don’t recall them purchasing this module. I brought back the file layout for the expense interface. I did not come back with a lot of specs for new projects. Believe it or not, they want another week of my time. Both Karen and Joanne (the Senior VP) seriously asked me to stay over the weekend and spend next week in Houston. I didn’t tell them this, but I don’t think that I could have lasted for 24 days.
01/07/01: I was surprised to discover that in 1997 Stage paid us over $8,000 for the expense payables, sales, MM Plus, and AdSEND (!) interfaces. No wonder we made so much money in those days. We have no choice but to give them the assistance they need to get the first three working. They don’t use AdSEND any more, thank goodness, and I am pretty certain that no one remembers that they paid for this. I don’t remember coding an expense interface for Stage, but we clearly did it in 1998. I will write up a quote to change it to work the way that the new documentation states.
Toni Young said that she thinks that Renee Mottu had not solved her possum problem.
I saw a sign at Stage Stores offering a $3,000 bonus to any employee that refers someone hired as a senior analyst in IS. The candidate must have five years of COBOL or Oracle experience.
Evidently I had already scheduled most of the rest of the month of January 2001 to travel to other clients so that if I had agreed to stay in Houston over the weekend and the following week, I would have been on the road for twenty-four days in a row! In those days we were charging $1,000 per day for my time. If Stage had still been in Chapter 11, I doubt that they would have proposed spending another $7,000 for another week of my presence. The bankruptcy court would have needed to approve the expense.
AdSend was a service offered by the Associated Press for sending the images of ad layouts to the newspapers. Hugo once told me that the company had twelve T-1 lines (TSI had one), and, according to him it was not nearly enough.
The neighborhood: Stage seemed to be a nice place to work. The headquarters was a fairly nice building located on the south side of Houston. They always provided me with a comfortable place to work, and there was ample parking in spaces reserved for vendors. The building also had a cafeteria that offered good food at very reasonable prices. I always ate lunch there, usually by myself. Many employees arrived at work early and ate breakfast there.
It was not too easy to reach by a car driven from the south. Just north of the building Main Street became a divided highway with restricted access. Since I always stayed in a hotel north of the building, I had to drive my rental car to the first exit, drive under the highway, and then take the access road back to Stage’s driveway.
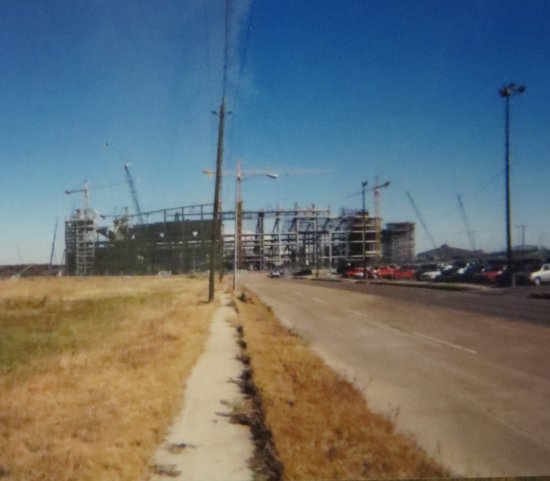
Most of Houston’s explosive growth had been in other directions. There was not much south of Stage’s location. However, just north of the building were the medical centers for which Houston was famous and Enron Field, which is where the Houston Astros played after the Astrodome was abandoned in 1999. I got to see (and photograph) the construction of the new stadium.

I usually stayed in a Hampton Inn a few blocks from the stadium. My favorite restaurant was a Mexican place called Marco’s. Located in a hard-to-reach strip mall near my hotel, it was where I first became acquainted with tacos al carbon, one of my favorite dishes. Marco’s had ridiculously low prices. I often told the manager that they should open restaurants in the northeast. They could have doubled their prices and still filled the place every night.
During a couple of multi-day trips to Stage I met up with Sue’s cousin, Mark Davis, for supper. He worked for Exxon Mobil. We usually at an Olive Garden. The conversation was better than the food.
I jogged on the streets near the hotel nearly every evening when I visited Stage. I worked out a route that kept me on streets that had very little traffic.
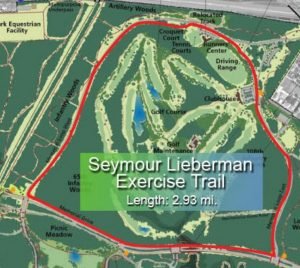
Eventually I discovered a delightful dirt track that surrounded a golf course in Memorial Park. I drove there every chance that I got. A loop around the track was a little less than three miles. I usually did two loops. There is no chance that I would ever move to Texas. However, if I did, it would be to Houston, and the primary motive would be to gain access to this track every day.
The people: I was quite surprised by the LinkedIn pages of the people with whom I worked at Stage. We had not done much work for the company after 2008 or so. Consequently, I really had no idea who was still working there after that. I discovered that many of them remained at Stage Stores quite a long time after I last saw them or talked with them.
TSI’s initial contact, Brenda, departed in 1998. I don’t know why she left Stage so soon after we did the installation. There might be a story there. I don’t recall ever hearing her name mentioned again.
I have many memories of Floyd. He was definitely a family man. He was always cheerful and business-minded. He always ate lunch at his desk. His office was not very large, but it had two doors, which he kept open. Some people used his office as a shortcut to get from one part of the marketing department to another. I was surprised when he and Toni seemed to switch jobs after Karen arrived. That was never explained to me. Floyd was employed by Stage Stores until 2011.
I was acquainted with Karen from her days at Foley’s. When she arrived at Stage, she made it clear to me that one of her top priorities was for the department to make better use of AdDept. A Republican, she assured all of us in January of 2001 that George W. Bush “will not be that bad.” After his two incredibly stupid wars and an economy that totally tanked while he and his cronies watched helplessly, most historian vehemently disagree.
Karen was, to my amazement, an avid biker—not mountain bikes, Harleys. She and her husband rode up to the big gathering in Sturgis, SD, at least once. I have always told people that if you saw me on a motorcycle, you can be certain that I will also be smoking a cigarette and showing off my piercings and tattoos.
Karen worked at Stage until 2013, twice as long as her stint at Foley’s. Her LinkedIn page lists no jobs after she left Stage Stores.
I remember that Hugo drove a Saturn—as did I during that period. His, however, was a coupe. If I had known that Saturn sold two-door cars, I would have bought one. Hugo stayed until 2017.
I did not really have much personal contact with Joanne, aside from that one meeting that they asked me to attend in 2001. I do remember that on one occasion I overheard Renee accosting her in the hallway. Renee said, quite loudly, “Joanne, I need a raise!” If Joanne replied, I did not hear the answer. Joanne left Stage Stores in 2012.
Toni apparently never left Stage Stores. The more that I worked with her the more that I respected her.
When I met Deidre I asked her if she was related to Diana Prince. She did not know whom I was talking about. I guess not everyone was a fan of Wonder Woman on TV and in the comic books.
I think that Deidre was our main contact when I showed the AxN12 system to the department in 2003 or 2004. They enthusiastically endorsed it and used it until they outsourced the buying of newspaper space to an outside company. Deidre left Stage in 2011.
Epilogue: I think that our last major dealings with Stage were the implementation of AxN and the Peebles project. Nevertheless, they were still using AdDept when TSI went out of business in 2014.
Unlike most retailers Stage Stores continued to expand in the twenty-teens by acquiring other chains. In 2017 Stage acquired the assets of the Gordman’s chain of department stores and quickly converted all of them to sell off-priced items. This worked so well that they began to convert most of their other stores to the same format. In the November 2019-February 2020 quarter sales were up 19 percent14.
Then the pandemic struck and Stage Stores was stuck with a lot of debt and 738 stores that could not be expected to generate any revenue in the immediate future. The price of the company’s stock plummeted. In May of 2020 Stage entered Chapter 11 again, and in August it announced that it was liquidating all of its holdings.
1. For some reason SRI insisted on a new contract every year. We had contracts with all of our AdDept clients, but all of the others were open-ended.
2. There is also an unrelated chain of department stores with the Bealls moniker that is based in Florida. My unsuccessful pitch to that company is detailed here.
3. Years after TSI was closed SRI moved to an office building at 2425 West Loop South. I tried to use Google Maps to find the Main Street building with which I was so familiar, but I failed. I think that it must have been demolished.
4. Brenda’s LinkedIn page is here. I had trouble remember her last name. I sent an email to Floyd Smith asking if he knew it. He replied, “Sure. She is also on Facebook..” Confused, I asked again. Floyd wrote, “Suire is her last name. Sorry about that spell check changed it last time.”
5. The Media Management Plus product was renamed SmartPlus. I think that this may have happened when the company was purchased by Arbitron, the rating service. On the Internet I found a very detailed description of what SmartPlus did. It is posted here.
6. Floyd’s LinkedIn page is here.
7. Hugo’s LinkedIn page can be viewed here.
8. In 1997 I was only 49. I was shocked that year to learn that Toni Young, who was younger than I was, had a grandchild who was by no means an infant. Her LinkedIn page is here.
9. I found no LinkedIn page for Renee Mottu. Her Facebook page is here. I was surprised to discover that it contained even less than mine does.
10. A great deal more has been written about the AdDept installation at Foley’s. The account is posted here.
11. Joanne Swartz’s LinkedIn page can be viewed here.
12. Deidre Prince’s LinkedIn page is here.
13. AxN was the name that I gave to TSI’s Internet program for management of insertion orders that AdDept users sent to newspapers. Its system design is explicated here. The marketing history is described here. Stage’s use of the system was one of the main reason that the number of subscribing newspapers grew so large—at one point over four hundred!
14. The Philadelphia Inquirer picked up this story from the Washington Post and posted it here.